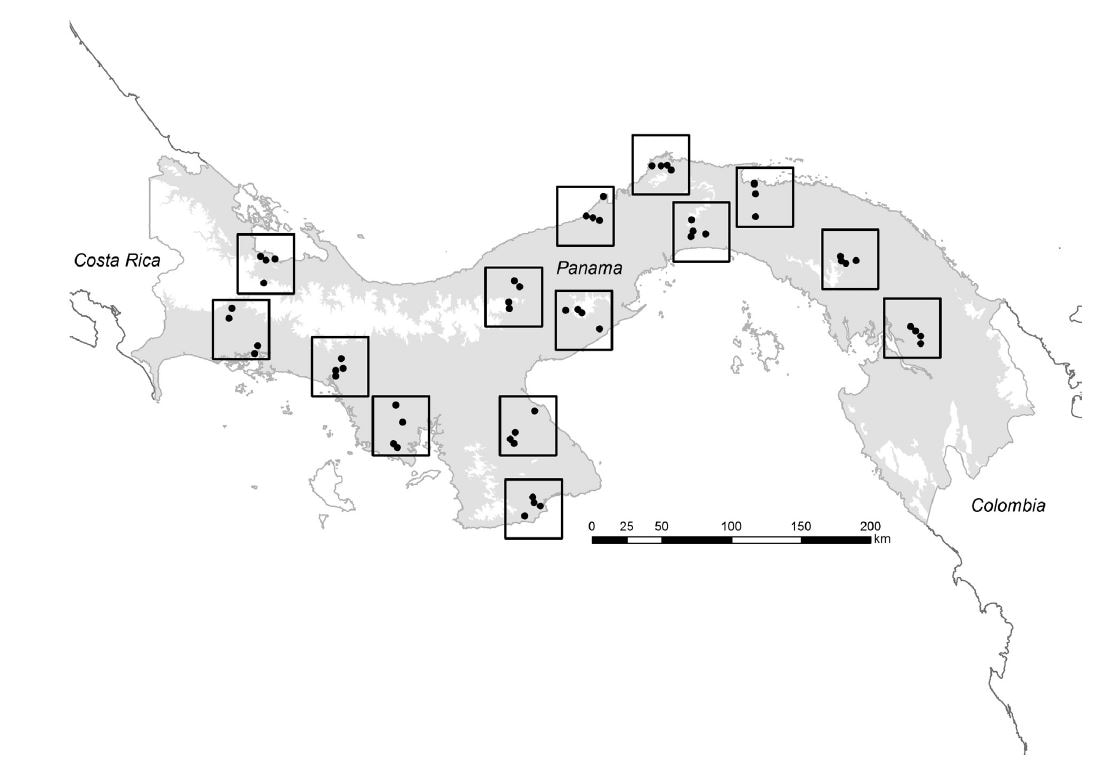
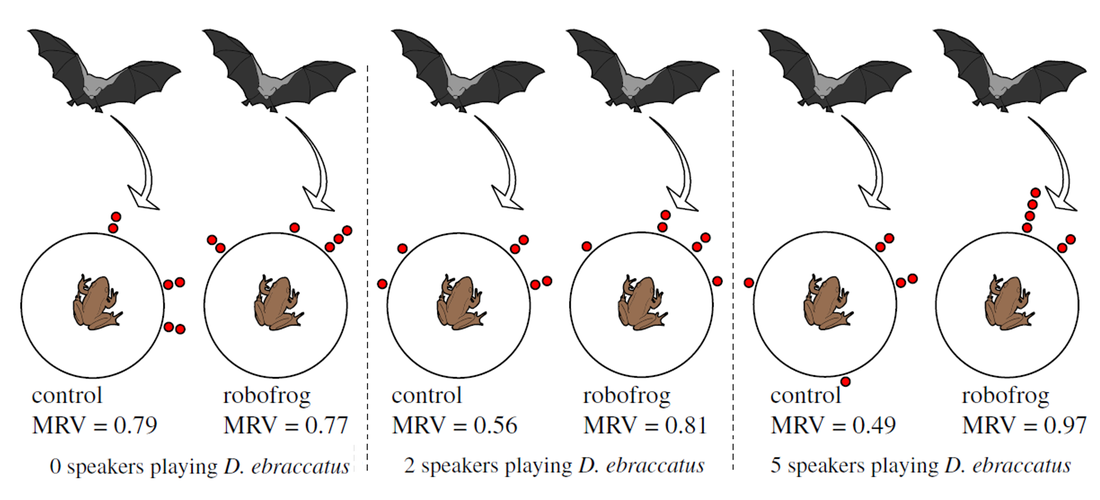
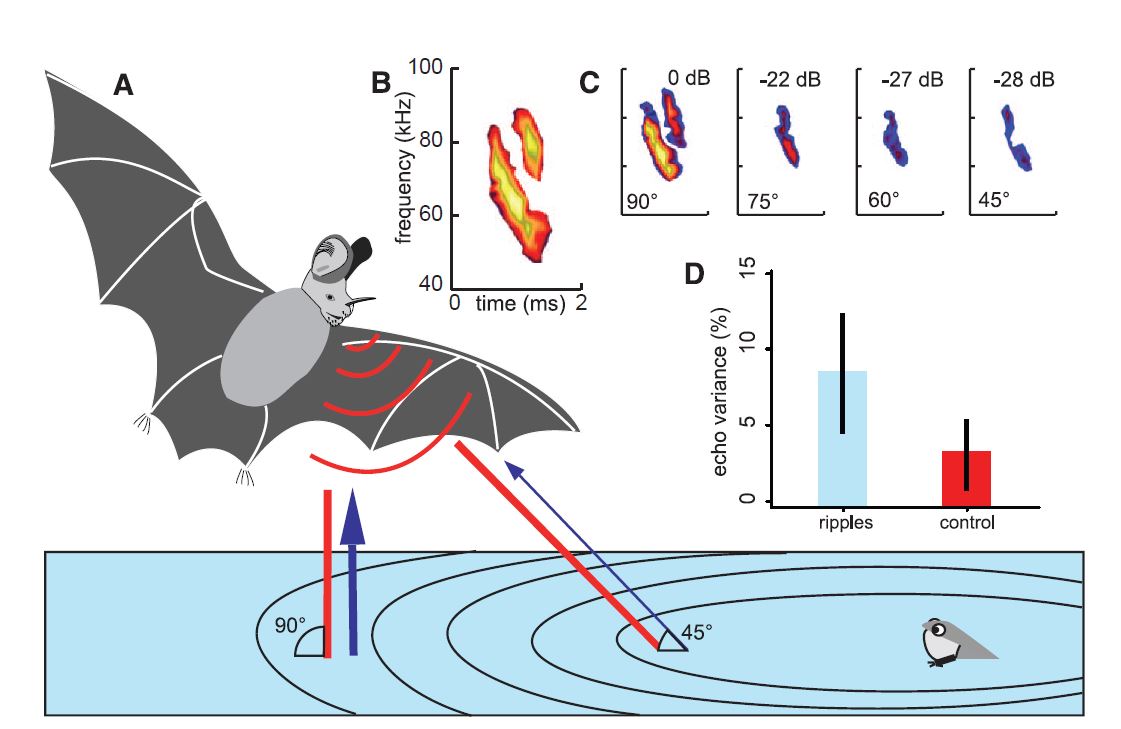
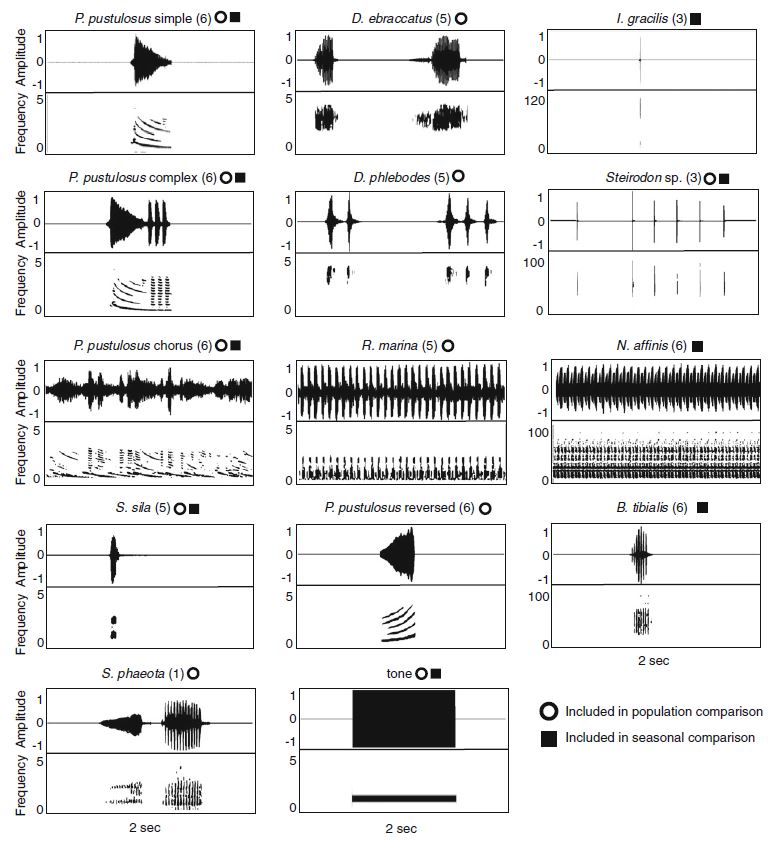
|
PUBLICATIONS
2024 Gómez-Feuillet LF, O’Mara MT, Page RA. In press. Leptodactylus savagei (Savage’s thin-toed frog). Diet. Herpetological Review. Kohles JE, Page RA, Wikelski M, Dechmann DKN. In press. Severe seasonal shifts in insect ephemerality drive bat foraging effort. Current Biology. 2023 Amichai E, Boerma DB, Page, RA, Swartz S, ter Hofstede HM. 2023. By a whisker: the sensory role of vibrissae in hovering-flight in nectarivorous bats. Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 290: 20222085. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2022.2085. PDF Bernal XE, Leavell BC, Page RA. 2023. Assessing patterns of eavesdropper risk on sexual signals and the use of meta-analysis in behavioural ecology: a comment on: ‘The exploitation of sexual signals by predators: a meta-analysis’ White et al. (2022). Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 290: 20221866. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2022.1866. PDF Dixon MM, Carter GG, Ryan MJ, Page RA. 2023. Spatial learning overshadows learning novel odors and sounds in both predatory and frugivorous bats. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. arad001. doi: 10.1093/beheco/arad001. PDF Page RA, Dechmann DKN, O'Mara MT, Tschapka M. 2023. Text to accompany a book of photography by Christian Ziegler. Bat Island: A Rare Journey into the Hidden World of Tropical Bats. San Rafael, CA: Insight Editions. On Amazon. 2022 Bernal XE, Page RA. 2022. Tactics of evasion: strategies used by signallers to deter eavesdropping enemies from exploiting communication systems. Biological Reviews. doi: 10.1111/brv.12904. PDF Bernal XE, Page RA. 2022. Editorial: How enemies shape communication systems: sensory strategies of prey to avoid eavesdropping predators and parasites. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 10. 989763. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2022.989763. PDF Bernal XE, Page RA (editors). 2022. eBook: How enemies shape communication systems: sensory strategies of prey to avoid eavesdropping predators and parasites. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. PDF Coss D, Ryan MJ, Page RA, Hunter K, Taylor R. 2022. Can you hear/see me? Multisensory integration of signals does not always facilitate mate choice. Behavioral Ecology. arac061. doi: 10.1093/beheco/arac061. PDF Cvecko P, Brändel S, Hiller T, Bechler J, Page RA, Tschapka M. 2022. New architecture of leaf-tents in American oil palms (Elaeis oleifera) used by the Pacific tent-making bat (Uroderma convexum) in Panama. Mammalia. doi: 10.1515/mammalia-2021-0058. PDF Dixon MM, Jones PL, Ryan MJ, Carter GG, Page RA. 2022. Long-term memory in frog-eating bats. Current Biology. 32, R557-R558. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.05.031. PDF James LS, Baier AL, Page RA, Clements P, Hunter KL, Taylor RC, Ryan MJ. 2022. Cross-modal facilitation of auditory discrimination in a frog. Biology Letters. 18: 20220098. PDF Kernan CE, Yiambilis AN, Searcy ZE, Pulica RM, Page RA, Caldwell MS. 2022. Mid-flight prey switching in the fringed-lipped bat (Trachops cirrhosus). The Science of Nature. 109: 43. PDF Larter L, Bernal XE, Page RA, Ryan MJ. Local competitive environment and male condition influence within-bout calling patterns in túngara frogs. Bioacoustics. 10.1080/09524622.2022.2070544. PDF Muñoz-Romo M, Cohen G, Page RA. 2022. Place your bets: a small prey faces large predators. Behaviour. 159: 989-997. doi: 10.1163/1568539X-bja10157. Coverage by the New York Times. PDF Muñoz-Romo M, Page RA, Vilar EM, Dewynter M, Lim BK. 2022. Revealing hidden sexually dimorphic male traits in the little white-shouldered bat, Ametrida centurio Gray 1847 (Chiroptera: Phyllostomidae). Mammalian Biology. doi: 10.1007/s42991-022-00227-5. PDF Page RA, Dechmann DKN. 2022. Primer: Roost making in bats. Current Biology. R1252-R1259. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.10.040. PDF. 2021 Brokaw, AF, Davis, E, Page, RA, Smotherman, M. 2021 Flying bats use serial sampling to locate odour sources. Biology Letters. 17, 20210430. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2021.0430. PDF Gessinger G, Page RA, Wilfert L, Surlykke A, Brinkløv S, Tschapka M. Phylogenetic patterns in mouth posture and echolocation emission behavior of phyllostomid bats. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 9. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2021.630481. PDF Geipel I, Lattenkamp EZ, Dixon MM, Wiegrebe L, Page RA. 2021. Hearing sensitivity: an underlying mechanism for niche differentiation in gleaning bats. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 118: e2024943118. PDF Hemingway, CT, Aversa J, Ryan MJ, Page RA. 2021. Context-dependent preferences in wild fruit bats. Animal Behaviour. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2021.06.016. PDF Hiller T, Vollstädt MGR, Brändel SD, Page RA, Tschapka M. 2021. Bat–bat fly interactions in Central Panama: host traits relate to modularity in a highly specialized network. Insect Conservation and Diversity. doi: 10.1111/icad.12508. PDF James LS, Halfwerk W, Hunter KL, Page RA, Taylor RC, Wilson PS, Ryan MJ. 2021. Covariation among multimodal components in the túngara frog’s courtship display. The Journal of Experimental Biology. 224. doi: 10.1242/jeb.241661. PDF Muñoz-Romo M, Page RA, Kunz TH. 2021. Redefining the study of sexual dimorphism in bats: following the odour trail. Mammal Review. doi: 10.1111/mam.12232. PDF Page RA, ter Hofstede HM. 2021. Sensory and cognitive ecology of bats. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics. 52: 541-562. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-012921-052635. PDF Razik I, Brown BKG, Page RA, Carter GG. 2021. Non-kin adoption in the common vampire bat. Royal Society Open Science. doi: 10.1098/rsos.201927. PDF Taylor RC, Wilhite KO, Ludovici RJ, Mitchell KM, Halfwerk W, Page RA, Ryan MJ, Hunter KL. 2021. Complex sensory environments alter mate choice outcomes. The Journal of Experimental Biology. 224: jeb233288. doi: 10.1242/jeb.233288. PDF 2020 Brändel SD, Hiller T, Halczok TK, Kerth G, Page RA, Tschapka M. 2020. Consequences of fragmentation for Neotropical bats: The importance of the matrix. Biological Conservation. 252: 108792. PDF Brown BKG, Leffer L, Valverde Y, Toshkova N, Nystrom J, Page RA, Carter GG. 2020. Do bats use guano and urine stains to find new roosts? Tests with three group-living bats. Royal Society Open Science. 7: 201055. doi: 10.1098/rsos.201055. PDF Carter GG, Farine DR, Crisp RJ, Vrtilek JK, Ripperger SP, Page RA. 2020. Development of new food-sharing relationships in vampire bats. Current Biology. 30: 1275-1279. e1273. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.01.055. PDF Flores V, Carter GG, Halczok TK, Kerth G, Page RA. 2020. Social structure and relatedness in the fringe-lipped bat (Trachops cirrhosus). Royal Society Open Science. 7: 192256. doi: 10.1098/rsos.192256. PDF Geipel I*, Kernan CE*, Litterer AS, Carter GG, Page RA#, ter Hofstede HM#. *Co-first authors; #Co-last authors. 2020. Predation risks of signalling and searching: bats prefer moving katydids. Biology Letters. 16: 20190837. doi: 0.1098/rsbl.2019.0837. PDF Hemingway C, Dixon MM, Page RA. 2020. The omnivore’s dilemma: the paradox of the generalist predators. In: Phyllostomid Bats, a Unique Mammalian Radiation (editors: TH Fleming, L Davalos, M Mello). University of Chicago Press. PDF Hemingway CT, Ryan MJ, Page RA. 2020. State-dependent learning influences foraging behaviour in an acoustic predator. Animal Behaviour. 163: 33-38. PDF Hermanns K, Marklewitz M, Zirkel F, Overheul GJ, Page RA, Loaiza JR, Drosten C, van Rij RP, Junglen S. 2020. Agua Salud alphavirus defines a novel lineage of insect-specific alphaviruses discovered in the New World. Journal of General Virology. 101: 96-104. PDF Hiller T, Brändel SD, Honner B, Page RA, Tschapka M. 2020. Parasitization of bats by bat flies (Streblidae) in fragmented habitats. Biotropica. 52: 488–501. doi: 10.1111/btp.12757. PDF Jones PL, Divoll TJ, Dixon MM, Aparicio D, Cohen G, Mueller U, Ryan MJ, Page RA. 2020. Sensory ecology of the frog-eating bat, Trachops cirrhosus, from DNA metabarcoding and behavior. Behavioral Ecology. 31: 1420–1428. doi: 10.1093/beheco/araa100. PDF Kohles JE, Carter GG, Page RA, Dechmann DKN. 2020. Social foraging bats discriminate between group members based on search-phase echolocation calls. Behavioral Ecology. 31: 1103-1112. doi: 10.1093/beheco/araa056. PDF Muñoz-Romo M, Flores V, Ramoni-Perazzi P, Page RA. 2020. The crust of a male: does size matter when females are fertile? Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 74: 151. doi: 10.1007/s00265-020-02914-0. PDF Page RA, Bernal XE. 2019. The challenge of detecting prey: Private and social information use in predatory bats. Invited review in ‘The role of sensory ecology and cognition in social decisions’ (eds. K Schneeberger, M Taborsky). Functional Ecology. 34: 344-363. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.13439. PDF; coverage in National Geographic. Paraskevopoulou S, Pirzer F, Goldmann N, Schmid J, Corman VM, Gottula LT, Schroeder S, Rasche A, Muth D, Drexler JF, Heni AC, Eibner GJ, Page RA, Jones TC, Müller MA, Sommer S, Glebe D, Drosten C. 2020. Mammalian deltavirus without hepadnavirus coinfection in the neotropical rodent, Proechimys semispinosus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 117: 17977-17983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2006750117. PDF Ripperger SP, Carter GG, Page RA, Duda N, Koelpin A, Weigel R, Hartmann M, Nowak T, Thielecke J, Schadhauser M, Robert J, Herbst S, Meyer-Wegener K, Wägemann P, Schröder-Preikschat W, Cassens B, Kapitza R, Dressler F, Mayer F. 2020. Thinking small: Next-generation sensor networks close the size gap in vertebrate biologging. PLOS Biology. 18: e3000655. PDF Stockmaier S, Bolnick DI, Page RA, Carter GG. 2020. Sickness effects on social interactions depend on the type of behaviour and relationship. Journal of Animal Ecology. 89: 1387-1394. doi: 10.1111/1365-2656.13193. PDF Stockmaier S, Bolnick DI, Page RA, Josic D, Carter GG. 2020. Immune-challenged vampire bats produce fewer contact calls. Biology Letters 16:20200272. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2020.0272 86. PDF Szczygieł H, Page RA. 2020. When the hunter becomes the hunted: foraging bat attacked by pit-viper at frog chorus. Ecology. The Scientific Naturalist. e03111. doi: 10.1002/ecy.3111. PDF ter Hofstede HM, Symes LB, Martinson SJ, Robillard T, Faure P, Madhusudhana S, Page RA. 2020. Calling songs of Neotropical katydids (Orthoptera, Tettigoniidae) from Panama. Journal of Orthoptera Research. PDF Velilla E, Muñoz M, Quiroga N, Symes L, ter Hofstede HM, Page RA, Simon R, Ellers J, Halfwerk W. 2020. Gone with the wind: Is signal timing in a neotropical katydid an adaptive response to variation in wind-induced vibratory noise? Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 74: 1-11. doi: 10.1007/s00265-020-02842-z. PDF 2019 Berrío-Martínez J, Kaiser S, Nowak M, Page RA, Carter GG. 2019. The role of past experience in development of feeding behavior in common vampire bats. PeerJ. 7:e7448. PDF Cronin AD, Ryan MJ, Page RA, Hunter KL, Taylor RC. 2019. Environmental heterogeneity alters mate choice behavior for multimodal signals. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 73:43. PDF Dixon MM, Hulgard K, Ratcliffe JM*, Page RA*. 2019. Habituation as an indicator of ecological relevance: Insights into the foraging ecology of a frog-eating bat. *Ratcliffe and Page contributed equally to this work. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 73: 101. doi: 10.1007/s00265-019-2700-1. PDF Flores EE, Batista A, Rodríguez V, Page RA. 2019. Vicente's poison frog (Oophaga vicentei) in the wild: calling activity, bioacoustics and diet. The Herpetological Bulletin. 149: 11-17. PDF. Flores E, Page RA, Aparicio D. 2019. Pristimantis moro. Herpetological Review. 50: 97-98. Flores V, Mateo JM, Page RA. 2019. The role of male forearm crust odor in fringe-lipped bats (Trachops cirrhosus). Behaviour. doi: 10.1163/1568539X-00003573. PDF Geipel I*, Amin B*, Page RA†, Halfwerk W†. (2019) Does bat response to traffic noise support the misleading cue hypothesis? Behavioral Ecology. 30: 1775–1781. doi: 10.1093/beheco/arz148. *Joint first authors; †Joint senior authors. PDF Geipel I, Smeekes MJ, Halfwerk W, Page RA. 2019. Noise as an informational cue for decision-making: the sound of rain delays bat emergence. The Journal of Experimental Biology. jeb.192005. PDF Gessinger G*, Gonzalez-Terrazas T*, Page RA, Jung K, Tschapka M. 2019. Unusual echolocation behaviour of the common sword-nosed bat Lonchorhina aurita: an adaptation to aerial insectivory in a phyllostomid bat? *Gessinger and Gonzalez-Terrazas contributed equally to this work. Royal Society Open Science. doi: 0.1098/rsos.182165. PDF Halfwerk W, Blaas M, Kramer L, Hijner N, Trillo PA, Bernal XE, Page RA, Goutte S, Ryan MJ, Ellers J. 2019. Adaptive changes in sexual signaling in response to urbanization. Nature Ecology & Evolution. doi:10.1038/s41559-018-0751-8. PDF Hemingway CT, Lea AM, Page RA, Ryan MJ. 2019. Effects of information load on response times in frogs and bats: mate choice vs. prey choice. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 73: 111. PDF Hemingway CT, Ryan MJ, Page, RA. 2019. Transitive foraging behaviour in frog-eating bats. Animal Behaviour. 154: 47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2019.05.005. PDF Legett HD, Page RA, Bernal XE. 2019. Synchronized mating signals in a communication network: the challenge of avoiding predators while attracting mates. Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 286. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2019.1067. PDF. Marklewitz M, Dutari LC, Paraskevopoulou S, Page RA, Loaiza JR, Junglen S. 2019. Diverse novel phleboviruses in sandflies from the Panama Canal area, Central Panama. Journal of General Virology. 100: 938-949. PDF Ripperger SP, Carter GG, Duda N, Koelpin A, Cassens B, Kapitza R, Josic D, Berrío-Martínez J, Page RA, Mayer F. 2019. Vampire bats that cooperate in the lab maintain their social networks in the wild. Current Biology. 10.1016/j.cub.2019.10.024. PDF. 2018 Carter GC, Forss S, Page RA, Ratcliffe JM. 2018. Younger vampire bats (Desmodus rotundus) are more likely to explore novel objects. PLOS ONE. 13(5): e0196889. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196889. PDF Estrada-Villegas S, Halczok TK, Tschapka M, Page RA, Brändel SD, Hiller T. 2018. Updated survey of the bats of Coiba National Park, Panama and their associated ectoparasites. Acta Chiropterologica. 20: 161–176. doi: 10.3161/15081109ACC2018.20.1.012. PDF Haelewaters D, Page RA, Pfister, D. 2018. Parasites of parasites of bats: morphological and molecular diversity of Laboulbeniales fungi associated with ectoparasite bat flies (Diptera: Nycteribiidae, Streblidae). Ecology and Evolution. doi: 0.1002/ece3.4359. PDF Halczok TK, Flores V, Brändel SD, Puechmaille SJ, Tschapka M, Page RA, Kerth G. 2018. Male-biased dispersal and the potential impact of human-induced habitat modifications on the Neotropical bat Trachops cirrhosus. Ecology and Evolution. doi: 10.1002/ece3.4161. PDF Hemingway CT, Ryan MJ, Page RA. 2018. Cognitive constraints on optimal foraging in frog-eating bats. Animal Behaviour. 143: 43-50. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2018.07.007. PDF Hiller T, Honner B, Page RA, Tschapka M. 2018. Leg structure explains host site preference in bat flies (Diptera: Streblidae) parasitizing neotropical bats (Chiroptera: Phyllostomidae). Parasitology. 1–8. doi: 10.1017/S0031182018000318. PDF Hiller T, Rasche A, Brändel SD, König A, Jeworowski L, O’Mara MT, Cottontail V, Page RA, Glebe D, Drexler JF, Tschapka M. 2018. Host biology and anthropogenic factors affect hepadnavirus infection in a Neotropical bat. EcoHealth, 1-13. doi: 10.1007/s10393-018-1387-5. PDF Kohles JE, Page RA, Dechmann DKN, O'Mara MT (2018) Rapid behavioral changes during early development in Peters' tent-making bat (Uroderma bilobatum). PLOS ONE 13(10): e0205351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205351. PDF Miller AJ, Page RA, Bernal XE. 2018. Exploratory behavior of a native anuran species with high invasive potential. Animal Cognition. 21: 55-65. doi: 10.1007/s10071-017-1138-y. PDF Page RA. 2018. Leveling the playing field: Comparative cognition studies in bats. Box in book chapter by Y Yovel, S Greif. Bat cognition. In: Field and Laboratory Methods in Animal Cognition (editors: F Amici, N Bueno-Guerra). Cambridge University Press. Patriquin KJ, Kohles J, Page RA*, Ratcliffe JM*. 2018. Bats without borders: predators learn novel prey cues from other predatory species. Science Advances. 4: eaaq0579. *Page and Ratcliffe contributed equally to this work. PDF Ryan MJ, Page RA, Hunter KL, Taylor RC. 2018. “Crazy love”—nonlinearity and irrationality in mate choice. Invited contribution to Cognitive Ecology issue of Animal Behaviour (eds JM Ratcliffe, R Dukas). doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2018.04.004. PDF Schmid J, Rasche A, Eibner G, Jeworowski L, Page RA, Corman VM, Drosten C, Sommer S. 2018. Ecological drivers of Hepacivirus infection in a neotropical rodent inhabiting landscapes with various degrees of human environmental change. Oecologia. doi: 10.1007/s00442-018-4210-7. PDF Stockmaier, S, Bolnick, DI, Page, RA, Carter, GG. 2018. An immune challenge reduces social grooming in vampire bats. Animal Behaviour. 140: 141-149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2018.04.021. PDF Symes L, Martinson S, Höger L-O, Page RA, ter Hofstede HM. 2018. Effects of predator cues on prey signaling behavior: bat echolocation and katydid calls in the Neotropical forest canopy. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 6:227. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2018.00227. PDF Vrtilek J, Carter GG, Patriquin KJ, Page RA*, Ratcliffe JR*. 2018. New method for rapid testing of social learning in vampire bats. Royal Society Open Science. *Page and Ratcliffe contributed equally to this work. 5: 172483. doi: 10.1098/rsos.172483. PDF Wasimuddin, Brändel SD, Tschapka M, Page RA, Rasche A, Corman VM, Drosten C, Sommer S. 2018. Astrovirus infections induce age-dependent dysbiosis in gut microbiomes of bats. ISME. doi:10.1038/s41396-018-0239-1. PDF 2017 Carter GG, Wilkinson GS, Page RA. 2017. Food-sharing vampire bats are more nepotistic under conditions of perceived risk. Behavioral Ecology. doi: 10.1093/beheco/arx006. PDF Flores EE, Page RA, Cisneros I, Rodriguez S. 2017. Oophaga vicentei (Vicente´s Poison Frog). Color change. Herpetological Review. 8: 166-167. PDF Flores V, Page RA. 2017. Novel odorous crust on the forearm of reproductive male fringe-lipped bats (Trachops cirrhosus). Journal of Mammalogy. 98: 1568-1577. doi: 10.1093/jmammal/gyx137. PDF, Nature Research Highlights PDF Gomes DGE, Halfwerk W, Taylor RC, Ryan MJ, Page RA. 2017. Multimodal weighting differences by bats and their prey: probing natural selection pressures on sexually selected traits. Animal Behaviour. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2017.10.011. PDF Hemingway C, Ryan MJ, Page RA. 2017. Rationality in decision-making in the fringe-lipped bat, Trachops cirrhosus. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 71: 94. doi: 10.1007/s00265-017-2321-5. PDF Jones PL, Hämsch F, Page RA, Kalko EKV, O’Mara MT. 2017. Foraging and roosting behavior of the fringe-lipped, Trachops cirrhosus, on Barro Colorado Island, Panamá. Acta Chiropterologica. 19: 337-346. doi: 10.3161/15081109ACC2017.19.2.010. PDF Taylor RC, Page RA, Klein BA, Ryan MJ, Hunter KL. 2017. Perceived synchrony of frog multimodal signal components is influenced by content and order. Integrative and Comparative Biology. doi: 10.1093/icb/icx027. PDF ter Hofstede HM, Voigt-Heucke SL, Lang A, Römer H, Page RA, Faure PA, Dechmann DKN. 2017. Revisiting adaptations of Neotropical katydids (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae) to gleaning bat predation. Neotropical Biodiversity. 3: 41-49. doi: 10.1080/23766808.2016.1272314. PDF 2016 Gomes DGE, Page RA, Geipel I, Taylor RC, Ryan MJ, Halfwerk W. 2016. Bats perceptually weight prey cues across sensory systems when hunting in noise. Science. 353: 1277-1280. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf7934. PDF, Supplemental Materials PDF Halfwerk W, Guerra MA, Lea AM, Page RA, Ryan MJ. 2016. Amplitude regulation in frogs reveals the ancestral state of the Lombard effect. Behavioral Ecology. 27: 669-676. doi: 10.1093/beheco/arv204. PDF Jones PL, Page RA, Ratcliffe JM. 2016. To scream or to listen? Prey detection and discrimination in animal-eating bats. In: Bat Bioacoustics (volume editors: B Fenton and A Grinnell; series editor: A. Popper). New York: Springer. pp. 93-116. PDF Page RA, Jones PL. 2016. Overcoming sensory uncertainty: factors affecting foraging decisions in frog-eating bats. In: Perception and Cognition in Animal Communication (volume editors, MA Bee and CT Miller), in the book series Animal Signals and Communication (series editors: PK McGregor and VM Janik). New York: Springer. pp. 285-312. PDF Ramakers JJC, Dechmann DKN, Page RA, O’Mara MT. (2016) Frugivorous bats prefer information from novel social partners. Animal Behaviour. 116: 83-87. PDF Ripperger S, Josic D, Hierold M, Koelpin A, Weigel R, Hartmann M, Page RA, Mayer F. 2016. Automated proximity sensing in small vertebrates: design of miniaturized sensor nodes and first field tests in bats. Ecology and Evolution. 6: 2179–2189. PDF Stange N, Page RA, Ryan MJ, Taylor RC. 2016. Interactions between complex multisensory signal components result in unexpected mate choice responses. Animal Behaviour. 134: 239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2016.07.005. PDF Symes LB, Page RA, ter Hofstede HM. 2016. Effects of acoustic environment on male calling activity and timing in Neotropical forest katydids. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 70: 1485-1495. DOI: 10.1007/s00265-016-2157-4. PDF Trillo PA, Bernal XE, Caldwell M, Halfwerk W, Owens M, Page RA. 2016. Collateral damage or a shadow of safety? The effects of signaling neighbors on the risks of parasitism and predation. Proceedings of the Royal Society Series B. 283: 20160343. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2016.0343. PDF Vencl FV, Ottens K, Dixon MM, Candler S, Bernal XE, Estrada C, Page RA. 2016. Pyrazine emission by a tropical firefly: an example of chemical aposematism? Biotropica. 48: 645–655. DOI 10.1111/btp.12336. PDF 2015 Bader, E, Jung, K, Kalko, EKV., Page, RA, Rodriguez, R, Sattler, T. 2015. Mobility explains the response of aerial insectivorous bats to anthropogenic habitat change in the Neotropics. Biological Conservation. 186: 97–106. PDF Bulbert, MW, Page, RA, Bernal, XE. 2015. Danger comes from all fronts: predator-dependent escape tactics of túngara frogs. PLOS ONE: 10(4): e0120546. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0120546. PDF Falk JJ*, ter Hofstede HM*, Jones PL, Dixon MM, Faure PA, Kalko EKV, Page RA. 2015. Sensory-based niche partitioning in a multiple predator-multiple prey community. Proceedings of the Royal Society Series B. 282: 20150520. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2015.0520. *Falk and ter Hofstede contributed equally to this work. PDF Fugère V, O'Mara MT, Page RA. 2015. Perceptual bias does not explain preference for prey call adornment in the frog-eating bat. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. DOI 10.1007/s00265-015-1949-2. PDF Rhebergen F, Taylor RC, Ryan MJ, Page RA, Halfwerk W. 2015. Multimodal cues improve prey localisation under complex environmental conditions. Proceedings of the Royal Society Series B. 282: 20151403. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2015.1403. PDF Stockmaier S, Dechmann DKN, Page RA, O’Mara MT. 2015. No fever and leukocytosis in response to a lipopolysaccaride challenge in an insectivorous bat. Biology Letters. 11: 20150576. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2015.0576. PDF 2014 Clarin TMA, Borissov I, Page RA, Ratcliffe JM, Siemers BM. 2014. Social learning within and across species: information transfer in mouse-eared bats. Canadian Journal of Zoology. 129-139. DOI 10.1139/cjz-2013-0211. PDF Halfwerk W, Dixon MM, Ottens K, Taylor RC, Ryan MJ, Page RA, Jones PL. 2014. Risks of multimodal signaling: bat predators attend to dynamic motion in frog sexual displays. Journal of Experimental Biology. 217: 3038-3044. DOI 10.1242/jeb.107482. PDF Halfwerk W, Jones PL, Taylor RC, Ryan MJ, Page RA. 2014. Risky ripples allow bats and frogs to eavesdrop on a multisensory sexual display. Science. 342: 413-416, DOI 10.1126/science.1244812. PDF, Supplemental Materials PDF Halfwerk W, Page RA, Taylor RC, Wilson PS, Ryan MJ. 2014. Cross-modal comparisons of signal components allow for relative distance assessment. Current Biology: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.05.068. PDF Jones PL, Ryan MJ, Page RA. 2014. Population and seasonal variation in response to prey calls by an eavesdropping bat. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 68: 605-615. DOI 10.1007/s00265-013-1675-6. PDF O’Mara MT, Dechmann DKN, Page RA. 2014. Frugivorous bats evaluate the quality of social information when choosing novel foods. Behavioral Ecology: 1–7. doi:10.1093/beheco/aru120. PDF Page RA, Ryan MJ, Bernal XE. 2014. Be loved, be prey, be eaten. In: Animal Behavior, vol 3. Case Studies: Integration and Application of Animal Behavior (ed., K. Yasukawa), New York: Praeger. pp. 123-154. PDF 2013 Clarin TMA, Ruczyński I, Page RA, Siemers BM. 2013. Foraging ecology predicts learning performance in insectivorous bats. PLoS ONE. 8: e64823. PDF Jones PL, Farris HE, Ryan MJ, Page RA. 2013. Do frog-eating bats perceptually bind the complex components of frog calls? Journal of Comparative Physiology A. 199: 279-283. PDF Jones PL, Ryan MJ, Flores V, Page RA. 2013. When to approach novel prey cues? Social learning strategies in frog-eating bats. Proceedings of the Royal Society Series B. 280: 20132330, http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2013.2330. PDF Surlykke A, Jakobsen L, Kalko EKV., Page RA. 2013. Echolocation intensity and directionality of perching and flying fringe-lipped bats, Trachops cirrhosus (Phyllostomidae). Frontiers in Physiology. 4:143, doi: 10.3389/fphys. 2013.00143. PDF 2012 Page RA, Schnelle T, Kalko EKV, Bunge T, Bernal XE. 2012. Sequential assessment of prey through the use of multiple sensory cues by an eavesdropping bat. Naturwissenschaften 99: 505-509. PDF Page RA*, von Merten S*, Siemers BM. 2012. Associative memory or algorithmic search: a comparative study on learning strategies of bats and shrews. Animal Cognition 15: 495-504. PDF, Coverage by Max Planck Institute for Ornithology. *Page and von Merten contributed equally to this work. 2011 Akre KL, Farris HE, Lea AM, Page RA, Ryan MJ. 2011. Signal perception in frogs and bats and the evolution of mating signals. Science 333: 751-752. PDF, Supplemental Materials PDF, Perspective PDF Jones PL, Page RA, Hartbauer M, Siemers BM. 2011. Behavioral evidence for eavesdropping on prey song in two Palearctic sibling bat species. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 65: 333-340. PDF 2009 Bernal XE, Page RA, Ryan MJ, Argo TF, Wilson PS. 2009. Acoustic radiation patterns of mating calls of the túngara frog (Physalaemus pustulosus): implications for multiple receivers. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 126: 2757-2767. PDF Siemers BM, Page RA. 2009. Behavioral studies of bats in captivity: methodology, training, and experimental design. In: Ecological and Behavioral Methods for the Study of Bats (ed. T. H. Kunz & S. Parsons), Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 373-392. PDF 2008 and earlier Page RA, Ryan MJ. 2008. The effect of signal complexity on localization performance in bats that localize frog calls. Animal Behaviour 76: 761-769. PDF Bernal XE, Page RA, Rand AS, Ryan MJ. 2007. Cues for eavesdroppers: do frog calls indicate prey density and quality? American Naturalist 169: 409-415. PDF Page RA. 2007. Prey-predator communication: for your sensors only. Dispatch for Current Biology 17: R965-R966. PDF Page RA, Ryan MJ. 2006. Social transmission of novel foraging behavior in bats: frog calls and their referents. Current Biology 16: 1201-1205. PDF, Dispatch PDF Page RA, Bernal XE. 2006. Túngara frogs. Quick guide for Current Biology 16: R979-980. PDF Page RA, Ryan MJ. 2005. Flexibility in assessment of prey cues: frog-eating bats and frog calls. Proceedings of the Royal Society Series B 272: 841-847. PDF Gabor CR, Page RA. 2003. Female preference for large males in sailfin mollies, Poecilia latipinna: the importance of predation pressure and reproductive status. Acta Ethologica 6: 7-12. PDF |
|
Proudly powered by Weebly